A new study links shorter sleep in teens to higher social media usage, affecting crucial brain regions. Learn how digital engagement impacts adolescent brain development.
Table of Contents
Introduction: The Impact of Social Media on Teen Sleep
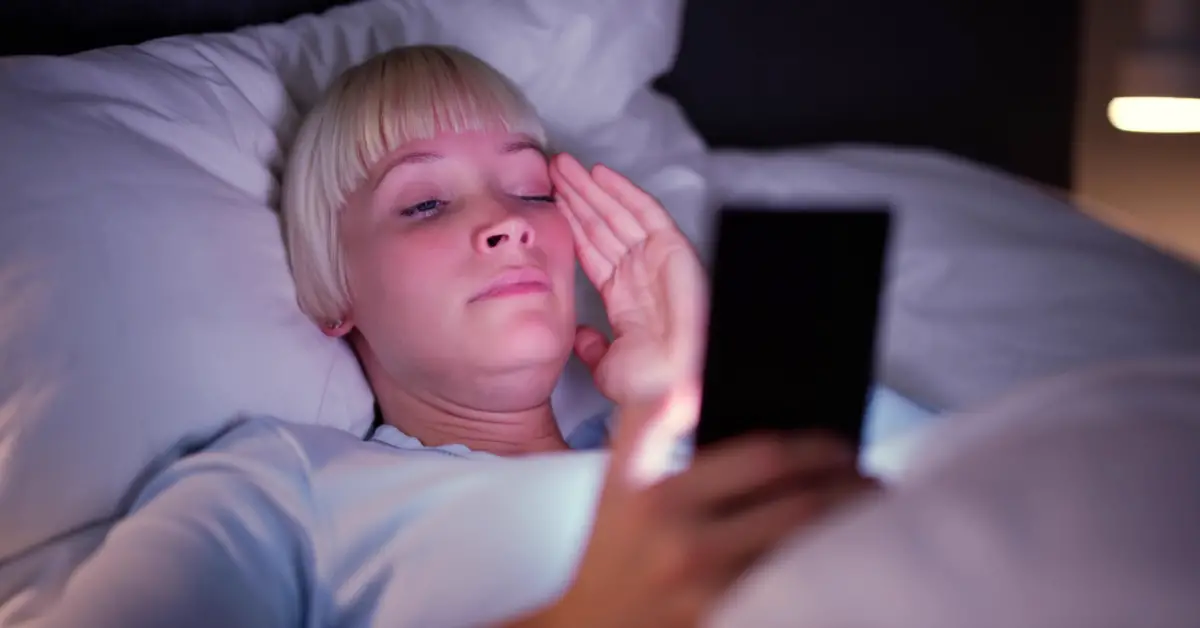
A groundbreaking study at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting uncovered a significant relationship between shorter sleep duration in teenagers and increased social media usage.
The research highlights the involvement of critical brain regions responsible for executive control and reward processing, emphasizing the profound impact of digital engagement on adolescent brain development.
Key Findings and Correlations
The study, conducted by researchers from SRI International and supported by the National Institutes of Health, examined data from 6,516 adolescents aged 10-14.
The findings revealed a clear correlation: shorter sleep duration is linked to higher social media usage.
The study focused on the frontolimbic brain regions, specifically the inferior and middle frontal gyri.
Key Brain Regions Involved
| Brain Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus | Inhibitory control |
| Middle Frontal Gyrus | Executive functions and reward assessment |
The Role of the Inferior and Middle Frontal Gyri
The inferior frontal gyrus, crucial for inhibitory control, helps regulate engagement with rewarding stimuli such as social media.
The middle frontal gyrus, involved in executive functions, is critical in balancing immediate rewards from social media with other priorities like sleep.
Orsolya Kiss, Ph.D., a cognitive psychology expert and research scientist at SRI International, commented, “Our findings suggest that poor sleep and high social media engagement could potentially alter neural reward sensitivity, impacting brain activity and development during adolescence.”
Study Methodology
The research utilized data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study.
Sleep duration was assessed using the Munich Chronotype questionnaire, while social media usage was measured through the Youth Screen Time Survey.
Functional MRI scans during the monetary incentive delay task analyzed brain activities in regions associated with reward processing.
Methodological Details
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Participants | 6,516 adolescents (ages 10-14 years) |
| Sleep Assessment | Munich Chronotype questionnaire |
| Social Media Usage | Youth Screen Time Survey |
| Brain Activity Analysis | Functional MRI scans during the monetary incentive delay task |
| Adjustments | Age, COVID-19 pandemic timing, socio-demographic characteristics |
Implications for Adolescent Health
The study’s results underscore the intricate interaction between digital engagement and sleep quality, with significant implications for adolescent brain development.
The findings highlight the need for evidence-based interventions to promote healthier digital and sleep habits among teenagers.
Dr. Kiss emphasized, “Understanding the specific brain regions involved in these interactions helps us identify potential risks and benefits associated with digital engagement and sleep habits. This knowledge is crucial for developing interventions aimed at promoting healthier habits.”
Recommendations for Healthier Sleep Habits
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) recommends that teenagers aged 13 to 18 should sleep 8 to 10 hours regularly.
They also encourage adolescents to disconnect from all electronic devices at least 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime to improve sleep quality.
Conclusion: Moving Forward
This study provides valuable insights into how social media usage and sleep duration influence adolescent brain development.
Understanding these interactions is vital for guiding interventions that foster healthier habits as these young brains undergo significant changes.
For more details on the study and its implications, visit the American Academy of Sleep Medicine.